Nucleotide Metabolism
Presentations | English
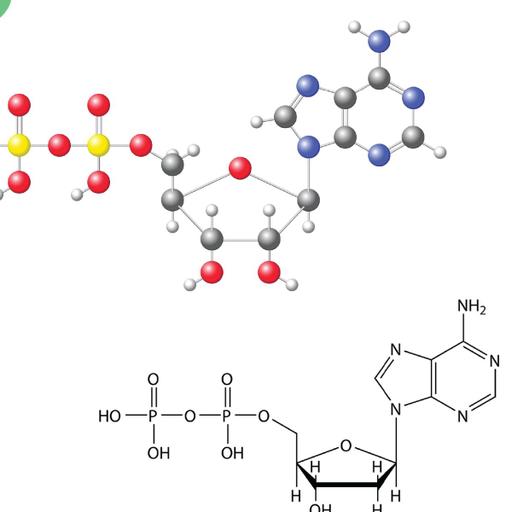
The life of any organism is dependent upon nucleotides, which are the basic building blocks of both deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). All cells within a given organism regardless of their size, will have a fixed amount of DNA residing within them. Nucleotide comprises of a deoxyribose (sugar), a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base. Nucleotide metabolism involves three amino acid donator reactions, serine to glycine reaction for methyl donation, aspartate to fumarate reaction for amine donation, and glutamine to glutamate reaction for amine donation. It is directly linked to cellular homeostasis as it is essential for physiological processes such as carbohydrate metabolism, oxidative phosphorylation, essential nucleotide biosynthesis, and signal transduction. The consequences of perturbations in purine and pyrimidine metabolism represent a diverse collection of disorders, differing in both their clinical manifestations and underlying molecular mechanisms.
32.50
Lumens
PPTX (65 Slides)
Nucleotide Metabolism
Presentations | English
