Kinetic Energy of Gases
Presentations | English
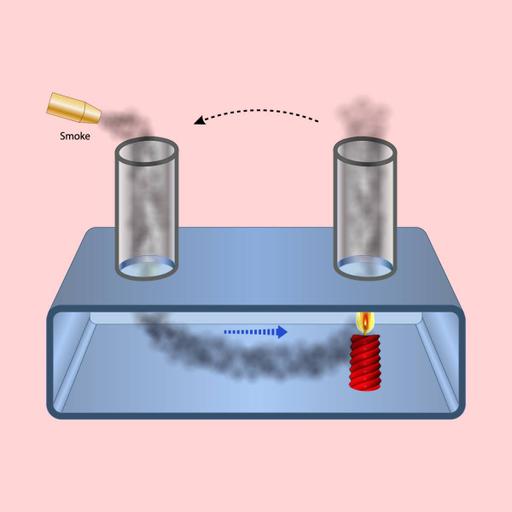
If you wish to explore the principles of gas molecules' motion and energy, this is the resource for you. This PowerPoint presentation covers the kinetic molecular theory, the relationship between temperature and kinetic energy, and the derivation of the kinetic energy formula. Additionally, it explains the implications for gas pressure, volume, and temperature relationships, offering a clear understanding of how molecular motion influences gas behavior. Download and make full use of the resource.
33.00
Lumens
PPTX (66 Slides)
Kinetic Energy of Gases
Presentations | English
