Biophysics of Photosynthesis
Presentations | English
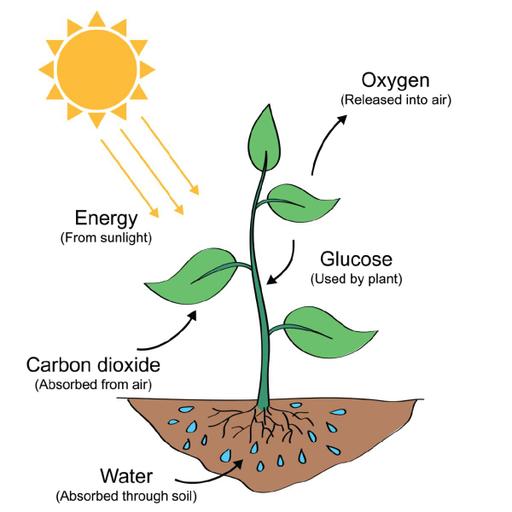
Photosynthesis is the procedure by which green plants, algae, and certain bacteria convert carbon dioxide from carbon from the sun into carbohydrates. Oxygen is a by-product of this procedure, which uses carbon dioxide and water. This process of strengthening the level of oxygen in the Earth's atmosphere is a direct or indirect source of energy for almost all living things. Chlorophyll A, chlorophyll B and carotene pigments in green particles help in photosynthesis. Chlorophyll-containing proteins absorb energy from light, and in plants. These proteins are found in chloroplasts, and in bacteria, plasma membrane. Some of the energy absorbed by chlorophyll is stocked as adenosine triphosphate, and the rest is used to remove electrons from water. With these free electrons, carbon dioxide and water are converted into complex organic compounds such as starch. Green plants, algae, and cyanobacteria undergo photosynthetic processes known as the Calvin cycle. But some bacteria, such as chlorophyll, undergo a reverse crepe cycle.
21.00
Lumens
PPTX (42 Slides)
Biophysics of Photosynthesis
Presentations | English
