Anatomy of Eye
Presentations | English
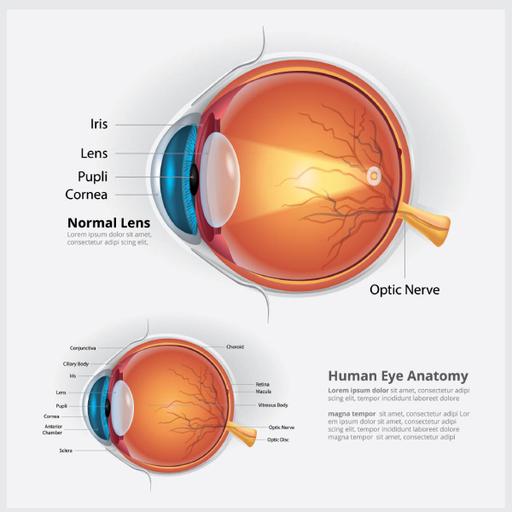
The eye is our organ of sight. The eye has a number of components which include but are not limited to the cornea, iris, pupil, lens, retina, macula, optic nerve, choroid and vitreous. The eye sits in a protective bony socket called the orbit. Six extraocular muscles in the orbit are attached to the eye. These muscles move the eye up and down, side to side, and rotate the eye. The extraocular muscles are attached to the white part of the eye called the sclera. This is a strong layer of tissue that covers nearly the entire surface of the eyeball. The surface of the eye and the inner surface of the eyelids are covered with a clear membrane called the conjunctiva. Light is focused into the eye through the clear, dome-shaped front portion of the eye called the cornea. Behind the cornea is a fluid-filled space called the anterior chamber. The fluid is called aqueous humor. The vitreous cavity lies between the lens and the back of the eye. Light that is focused into the eye by the cornea and lens passes through the vitreous onto the retina which is the light-sensitive tissue lining the back of the eye.
Free
PPTX (28 Slides)
Anatomy of Eye
Presentations | English
