Action Potential
Presentations | English
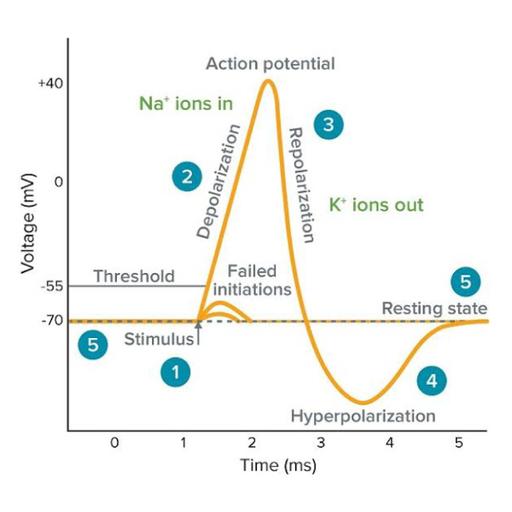
An action potential is a sudden increase and fall in voltage or membrane potential across a cell membrane. These are primarily neurons or muscle cells. When a cell is not sending signals, it is at its resting potential. When different ions cross the cellular membrane, potential is generated. Because there is less inside than outside, a stimulus causes sodium to rush inside the cell membrane. Because sodium is positive, the cell becomes positive and depolarized. When potassium rushes out of the cell, depolarization is reversed, and sodium channels close, resulting in repolarization. Explore this PPT to learn more about the subject.
Free
PPTX (13 Slides)
Action Potential
Presentations | English
